"It is complicated," I replied.
In the first place, I am not sure if I have enough expertise to talk about this. On top of that, the usual complaint is that my responses are always way longer than what the questioner had in mind. I suppose I don't like to merely give the bottom-line, consistent with my philosophical approach to life that it is never merely about the destination but also about the journey itself.
So, without any expertise I launched into a lengthy explanation.
"It is not as if things are black-and-white when it comes to being gay. Most researchers now talk in terms of sexual fluidity" I started.
I keenly watched out for any glazed expression. Or the eyeball disappearing after having been rolled way up. No signs. There was an attentive posture. I got encouraged.
"The this-or-that approach is modern. In olden times, it seems like people might have been way less rigid about this than we are now." I went on and on and on. Interestingly enough, there were even questions posed and it became an interactive session!
A few days later, I read this awesome essay by Siddhartha Mukherjee, on sex, gender, and gender identity. Yes, the same Mukherjee whose book on cancer won him a Pulitzer. This essay is an excerpt from another book of his: The Gene: an Intimate History.
Mukherjee writes:
The distinction between the three words is relevant to this discussion. By sex, I mean the anatomic and physiological aspects of male versus female bodies. By gender, I am referring to a more complex idea: the psychic, social, and cultural roles that an individual assumes. By gender identity, I mean an individual’s sense of self (as female versus male, as neither, or as something in between).Across the world, as we begin to move away from the old collective arrangements that denied an individual's sense of self, we are beginning to see even the supposedly conservative societies having to face the complexity of sex, gender, and gender identity.
Strictly from a genetic perspective:
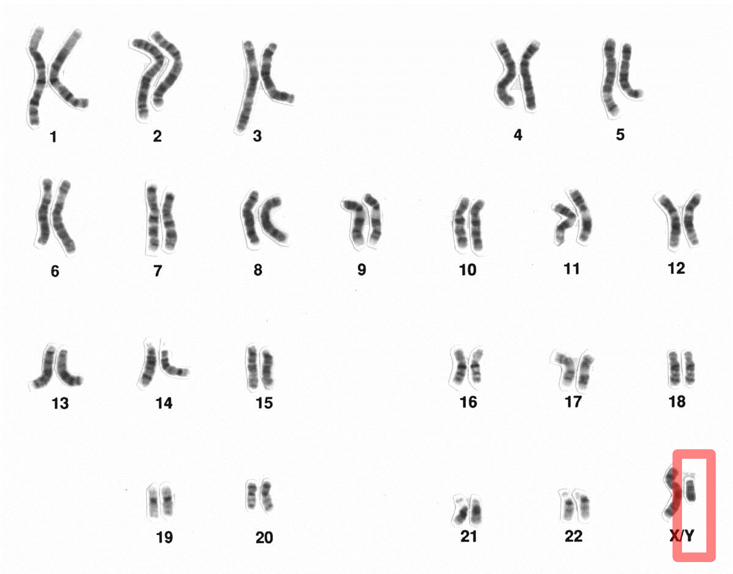
Sex, one of the most complex of human traits, is unlikely to be encoded by multiple genes. Rather, a single gene, buried rather precariously in the Y chromosome, must be the master regulator of maleness. Male readers of that last paragraph should take notice: We barely made it.If you are a long-time reader of this blog, you know about the geographic migratory path of my maleness that came from the African Savannah.
Anyway, even from a genotype/phenotype perspective--without the cultural/socialization aspects--the story is complex:
In 1955, Gerald Swyer, an English endocrinologist investigating female infertility, had discovered a rare syndrome that made humans biologically female but chromosomally male. “Women” born with “Swyer syndrome” were anatomically and physiologically female throughout childhood, but did not achieve female sexual maturity in early adulthood. When their cells were examined, geneticists discovered that these “women” had XY chromosomes in all their cells. Every cell was chromosomally male—yet the person built from these cells was anatomically, physiologically, and psychologically female. A “woman” with Swyer syndrome had been born with the male chromosomal pattern (i.e., XY chromosomes) in all of her cells, but had somehow failed to signal “maleness” to her body.Imagine that! What a complication, right? In the extended family, we have had at least two cases of girls who were biologically girls but who never reached that sexual maturity in their teens. I wonder if they too could have been chromosomally male?
But do not jump to conclusions about this chromosomal aspects:
Women with Swyer syndrome are not “women trapped in men’s bodies.” They are women trapped in women’s bodies that are chromosomally male (except for just one gene).Pause for a second and think about this: "women trapped in women’s bodies that are chromosomally male (except for just one gene)" Head-spinning, right?
How can we reconcile this idea—of a single genetic switch that dominates one of the most profound dichotomies in human identity—with the fact that human gender identity in the real world appears in a continuous spectrum? Virtually every culture has recognized that gender does not exist in discrete half-moons of black and white, but in a thousand shades of gray.Every single fucked up homophobe, condemning people to hell-on-earth based on some fucked up religious interpretation, should be locked up in a room until they read and understand all these complex issues.
At the top of the cascade, nature works forcefully and unilaterally. Up top, gender is quite simple—just one master gene flicking on and off. If we learned to toggle that switch—by genetic means or with a drug—we could control the production of men or women, and they would emerge with male versus female identity (and even large parts of anatomy) quite intact. At the bottom of the network, in contrast, a purely genetic view fails to perform; it does not provide a particularly sophisticated understanding of gender or its identity. Here, in the estuarine plains of crisscrossing information, history, society, and culture collide and intersect with genetics, like tides. Some waves cancel each other, while others reinforce each other. No force is particularly strong—but their combined effect produces the unique and rippled landscape that we call an individual’s identity.Like I said, it is complicated.
 |
| Source |


